|
Software Frameworks and Toolsets for Deep Learning-based Vision Processing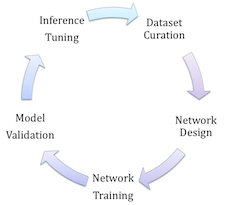
Deep learning is an increasingly popular and robust alternative to classical computer vision algorithms. This technical article from the Embedded Vision Alliance and member companies Au-Zone Technologies, BDTI, MVTec, Synopsys and Xilinx covers the leading deep learning software frameworks, the reasons for their abundance, and guidelines for selecting among the candidates for a particular application. It also covers "middleware" utilities that optimize a framework for use in an embedded implementation, comprehending factors such as data types and bit widths, as well as available heterogeneous computing resources. And for developers in specific markets and applications, application-specific toolsets that incorporate deep learning techniques can provide an attractive alternative to more general-purpose frameworks.
Accelerating Deep Learning Using FPGAs
While large strides have recently been made in the development of high-performance systems for neural networks based on multi-core technology, significant challenges in power, cost and, performance scaling remain. Field-programmable gate arrays (FPGAs) are a natural choice for implementing neural networks because they can combine computing, logic, and memory resources in a single device. In this presentation, Bill Jenkins, Senior Product Specialist at Intel, describes the company's scalable convolutional neural network reference design for deep learning systems using the OpenCL programming language. Jenkins benchmarks performance using several popular CNN benchmarks: CIFAR-10, ImageNet and KITTI.
|
|
Understanding Camera Subsystems for Your Embedded Vision System and Making the Right Choice
More than ever, you have a wide range of camera subsystems to choose from. At one end of the spectrum, a system designer can utilize a complete, external camera, as is often done in industrial applications. At the other, one could select an image sensor and design all of the necessary camera functionality as part of the end-product design. Of course, there are several options in-between these two points. This talk from Gerrit Fischer, Head of Product Market Management at Basler, provides insight into the different options available for an embedded vision architecture, advantages and disadvantages, and a framework to help your team understand the business and technical tradeoffs and determine which approach is best for a specific end-product.
Memory Innovation for Embedded Vision Systems
In this presentation, Jin Kim of Samsung Electronics explains the memory needs of embedded vision applications and how memory is evolving to meet those needs.
|
