This blog post was originally published at TechNexion’s website. It is reprinted here with the permission of TechNexion.
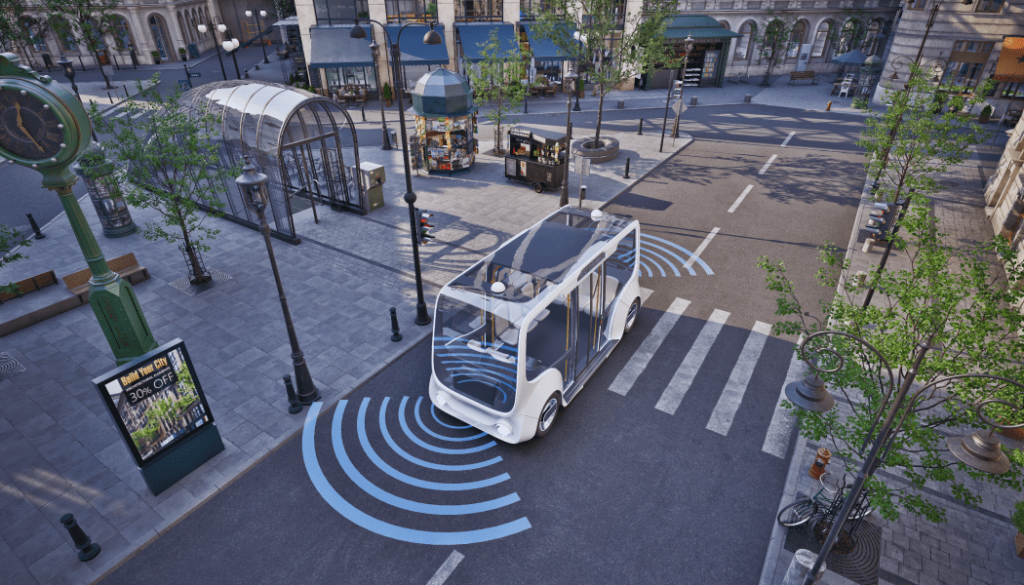
The transportation sector has always been at the forefront of technological advancements, and the emergence of the “Smart Bus” system is a testament to this evolution. This innovative system is not just about enhancing the passenger experience but also about leveraging real-time data for future enhancements and planning.
This system is revolutionizing public transportation, combining embedded systems with camera technology to create intelligent vehicles. These buses are equipped with cameras that capture and analyze their surroundings in real-time, allowing them to respond more quickly and efficiently. This fusion of advanced technology is paving the way for a new era of transit, one in which passengers can travel faster, safer, and more comfortably. Join us on this journey into the future of public transportation to discover how cameras and embedded systems are transforming the way we travel.
What is the “Smart Bus” System?
The “Smart Bus” system represents the next generation of public transportation, integrating advanced technologies for a streamlined experience. It is a comprehensive solution that optimizes passenger experiences by providing networking services in innovative and cost-effective ways. It employs various networking devices, such as 5G WiFi routers, information display systems, and in-vehicle cameras, to enhance passenger services and safety. With embedded systems and sophisticated camera technology, it can monitor, analyze, and respond to real-time data – from fare collection and passenger flow to road conditions and safety measures.
Key Components of the Smart Bus System
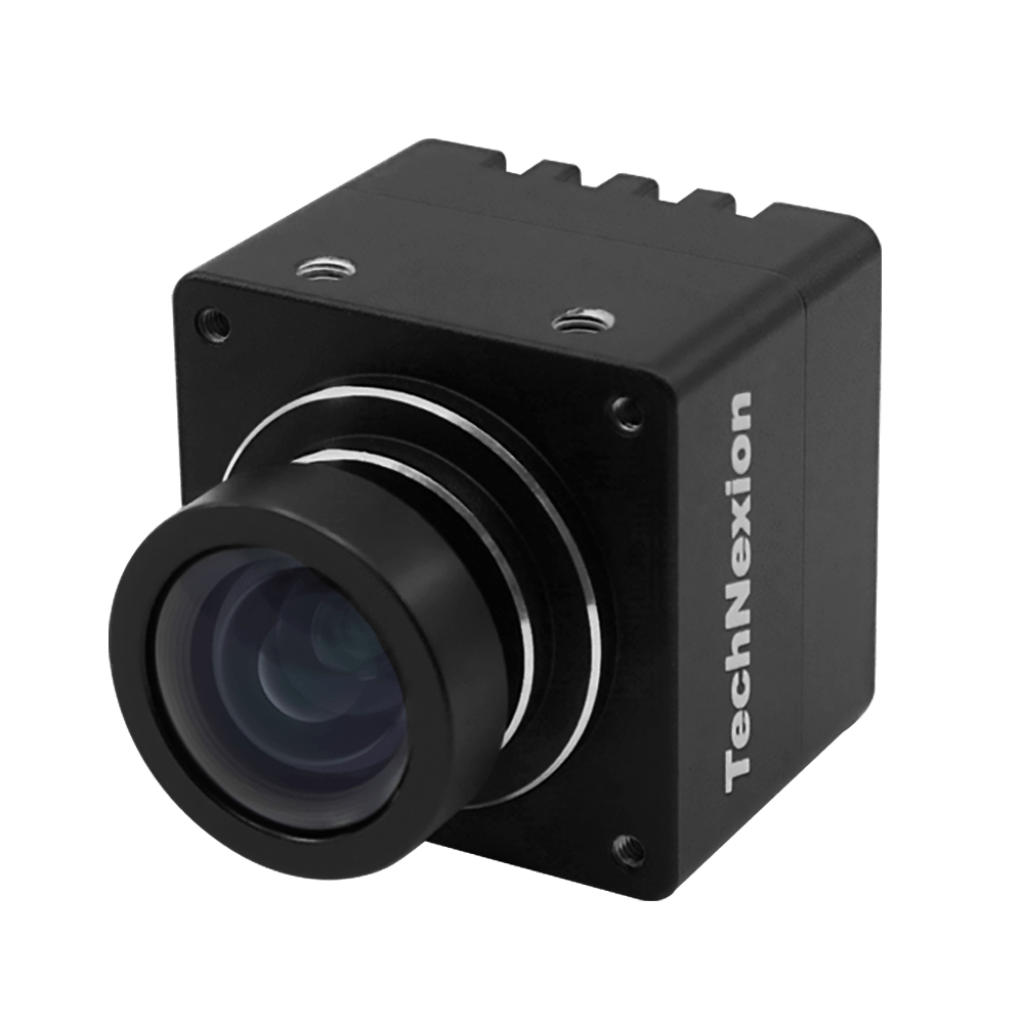

VCI-AR0821-SL
- Smart Bus core: The Smart Bus Core acts as the central unit that controls all the networking devices on the bus. It can be controlled either individually or in groups via a central computer, thanks to a specially designed interface. This ensures seamless operations and real-time data collection, such as fare records, passenger flow, and road conditions, which will enable future improvements and planning.
- Smart Bus camera: Cameras on the Smart Bus are not just for surveillance. They help with passenger counting & analysis, creating a 360-degree surround view, and driver status monitoring (DSM). This data is invaluable for future planning and ensuring the safety of passengers.Depending on the purpose of the camera, its features would also change. For example, the DSM camera will need a high frame rate of 60 fps or more. It also uses 940nm infrared fill light combined with an infrared lens, which can effectively improve brightness in a dark environment. The use of this wavelength also ensures that interference from bright sunlight does not affect the quality of imaging.
- Smart displays: With the integration of smart signage advertising, buses can now display targeted advertisements based on the pedestrians outside. This not only enhances the advertising experience but also ensures that ads are relevant to the viewers.
- 5G Connectivity: 5G WiFi routers on the Smart Bus ensure that there is always a reliable and uninterrupted communication channel. This is crucial for real-time data collection and passenger networking services.
Camera Features in Smart Buses
Cameras play a pivotal role in the Smart Bus system. The integration of AI with embedded cameras has revolutionized traffic management systems.
Here are some critical features of these vision systems across the 3 major purposes for which cameras are used.
- Driver Status Monitoring: Driver status monitoring ensures that the driver doesn’t doze off while driving. This is a lifesaver, particularly in long-distance driving, where the likelihood of the driver falling asleep is much higher. Modern vehicle features like cruise control also increase this risk, though it offers a certain level of convenience. Cameras help to prevent accidents by making sure that the driver is always awake and active. Given below are the key features of a camera used for driver status monitoring:
- Shutter Type: A global shutter is essential to capture minute details like eye blinking without rolling shutter artifacts.
- Chroma: Monochrome cameras are enough in most cases. In addition, they tend to offer better sensitivity compared to their color counterparts.
- IR Sensitivity: Ensures clear visuals in low light conditions inside the bus, especially during nighttime. This also helps to clearly capture the features of the eye – which is critical in detecting sleep or exhaustion. In order to avoid interference from sunlight, an IR light source of wavelength 940nm is typically used. This, in turn, demands a camera with high sensitivity in that spectrum.
- Resolution: A maximum resolution of 5MP is generally sufficient.
Apart from these, the strobe function is a good to have in these cameras since that helps in synchronized operations of the camera and the light system.
- Blind Spot Detection: Buses are large. It is impossible for the driver to get a complete view of the vehicle’s surroundings. This can often lead to accidents and collisions. 360-degree surround view cameras are used to help with detecting blind spots – thereby significantly increasing passenger and pedestrian safety. Here are some of the key camera features that are critical for a blind spot detection system:
- Multi-Camera System: At least four cameras are required for comprehensive coverage.
- Synchronization: All cameras need to be in sync for accurate data collection.
- Interface: For long distances, SerDes interfaces like FPD Link or GMSL are recommended.
- Processor Compatibility: The system has to be compatible with processors such as NVIDIA, TI, and others for onboard image processing.
- HDR: Ensures clear visuals in varying outdoor lighting conditions.
- Low Latency: Crucial for displaying near-real-time video on the driver’s display screen.
- Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS): In ADAS, cameras help in giving collision and lane departure warnings. Some of the camera-related features of these systems are:
- Depth Sensing: These might be required for detecting obstacles.
- Long Distance Interface: Essential for seamless communication.
- HDR: For clear visuals in bright light conditions
- Multi-Camera Sync: for making sure that all necessary sides are covered.
- Low Latency: Crucial for near-real-time display for the driver.
How Cameras and AI Combine to Power Smart Buses
Integration of cameras and AI in public transportation – particularly smart buses – work hand in hand to enhance commuter journeys in real-time decision-making processes as well as improve overall commuter experiences. Here is an in-depth exploration of their collaboration to power smart buses:
- Real-time data analysis: Cameras on board continuously capture data both inside and outside, which AI algorithms process in real time to offer actionable insights – for instance, passenger count can help maintain social distancing norms or determine when a bus is full.
- Driver monitoring for safety: Advanced cameras equipped with AI software can use advanced techniques to track drivers’ behaviors, such as eye movement, posture, and facial expressions, to detect signs of fatigue, distraction, or medical emergencies that require immediate action from either them or from control centers. These analyses can then alert both of them.
- Predictive maintenance: Cameras installed strategically around a bus can detect wear-and-tear or potential problems and use artificial intelligence (AI) to predict when parts may break or require service – providing proactive repairs while decreasing unexpected breakdowns.
- Enhancing passenger experience: Cameras can capture passenger demographics and behaviors for processing by AI systems to display targeted advertisements on bus screens or adjust lighting/temperature based on the number and type of passengers on board.
- Traffic and route optimization: Cameras mounted at the front and sides of a bus can monitor road conditions, traffic patterns, and potential obstacles, and suggest optimal routes that avoid jams or roadblocks. AI algorithms then analyze this data to produce results that suggest ideal alternatives – potentially saving lives while cutting congestion costs significantly.
- Safety and security enhancements: Cameras in buses can detect suspicious activities such as unattended bags or potential threats and notify either security personnel or drivers immediately so all passengers remain secure and safe. This ensures everyone remains protected.
- Obstacle and pedestrian detection: Smart buses equipped with depth cameras and AI can use artificial intelligence (AI) to recognize obstacles on the road or pedestrians crossing unexpectedly and take preventative steps such as slowing down, braking, or alerting their driver, improving safety measures.
- Blind spot monitoring: We already touched upon this. Security cameras installed around a bus can monitor areas that fall outside the field of view of its driver and alert him or her immediately should there be anything in a blind spot – particularly vital when changing lanes or making turns. AI technology alerts the driver if something enters these blind spots that should not.
Applications of the “Smart Bus” System: Bridging Smart Traffic and Smart Cities

The integration of advanced technologies in the “Smart Bus” system has had significant applications in smart traffic and smart cities. From enhancing the passenger experience to improving urban living and infrastructure, its impact reaches far beyond just one sector. Here are three key applications of the “Smart Bus” system.
- Intelligent Traffic Management
- Real-time route optimization: Modern traffic management systems use AI and ML-based algorithms to analyze videos and images. Smart buses can integrate with these systems, allowing for features like automatic toll payments, parking assistance, and even communication with traffic lights for optimal signal timings.
- Predictive maintenance: As mentioned earlier, by continuously tracking bus health and performance metrics, predictive maintenance systems can accurately forecast when parts may fail or require service; this allows operators to avoid unexpected breakdowns while increasing traffic flow with greater ease.
- Safety improvements: Advanced cameras can identify potential road hazards such as pedestrians unexpectedly crossing streets or vehicles braking abruptly, alerting the bus driver or even taking corrective actions that reduce risk and significantly lessen risk. This system has proven its worth time after time in helping prevent accidents from happening.
- Seamless integration with smart city infrastructure
- Data sharing: “Smart Bus” technology can share its real-time data with a central smart city database to facilitate urban planning efforts, from optimizing traffic light patterns based on bus routes to planning new transit hubs.
- Environmental monitoring: Outfitted with environmental sensors, the bus can monitor air quality, temperature, and other environmental aspects as it travels through cities. City planners can then use this data to address pollution hotspots or any environmental concerns identified during its route.
- Energy efficiency: Consistent with smart city sustainability goals, “Smart Bus” may be designed to use renewable sources of power, which reduce the carbon footprint and analyze its energy consumption for further efficiency improvement.
- Enhanced urban connectivity and accessibility
- Smart stops: Bus stops can now come equipped with digital displays showing real-time bus arrival times, route changes, or delays so passengers are kept up-to-date and can better plan their trips. This enables passengers to stay informed and plan.
- Integrated fare systems: The “Smart Bus” can integrate seamlessly with a city’s digital payment system, giving passengers a single method for paying for multiple modes of public transport with just one payment method.
- Accessibility features: For elderly or differently-abled passengers, public transit buses can offer accessibility features like automated ramps, visual and auditory announcements, and priority seating that make public transport more inclusive.
In conclusion, with its advanced features and data collection capabilities, the Smart Bus system promises a safer and more efficient commuting experience for all. As technology continues to evolve, we can only expect these systems to become more sophisticated, offering unparalleled benefits to both passengers and transportation authorities. Cameras and embedded vision play a critical role in this transformation.
TechNexion is at the forefront of this revolution, offering embedded cameras and system-on modules tailored for modern traffic management systems. Our products boast high resolutions of up to 13 MP, high dynamic range, NIR sensitivity, interchangeable lenses, and support for AI processors like NVIDIA Jetson and TI Jacinto TDA4VM. With a commitment to innovation, TechNexion is the go-to choice for those looking to integrate the best camera solutions into their smart traffic management devices.


