This blog post was originally published at Qualcomm’s website. It is reprinted here with the permission of Qualcomm.
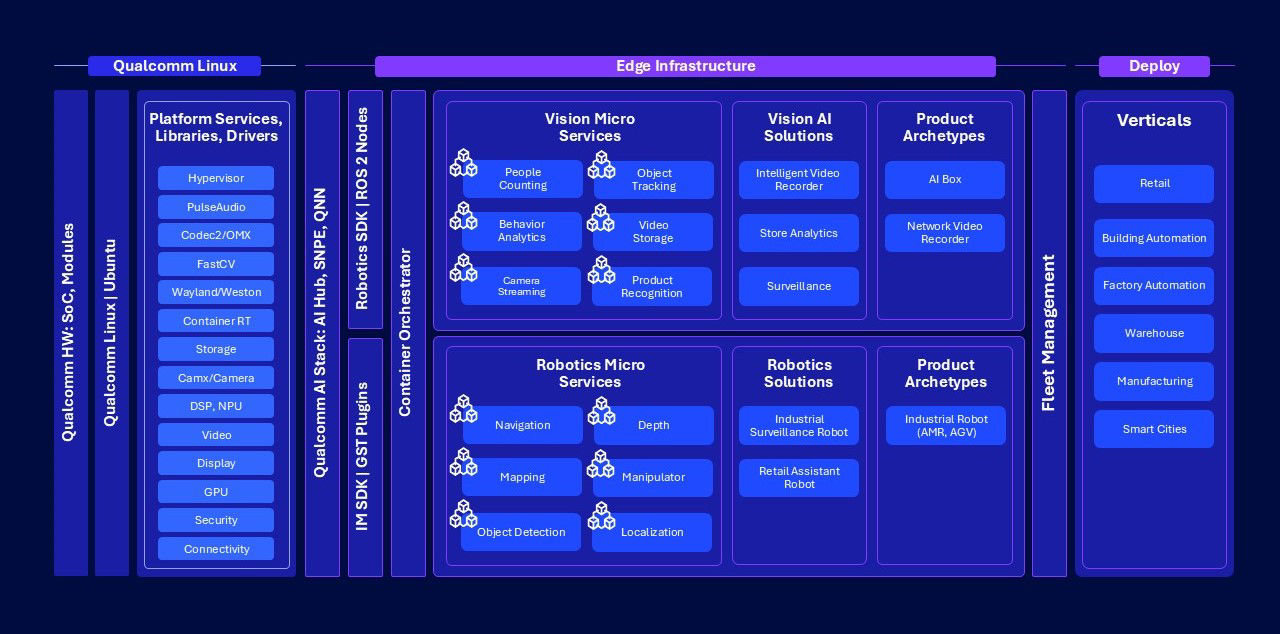
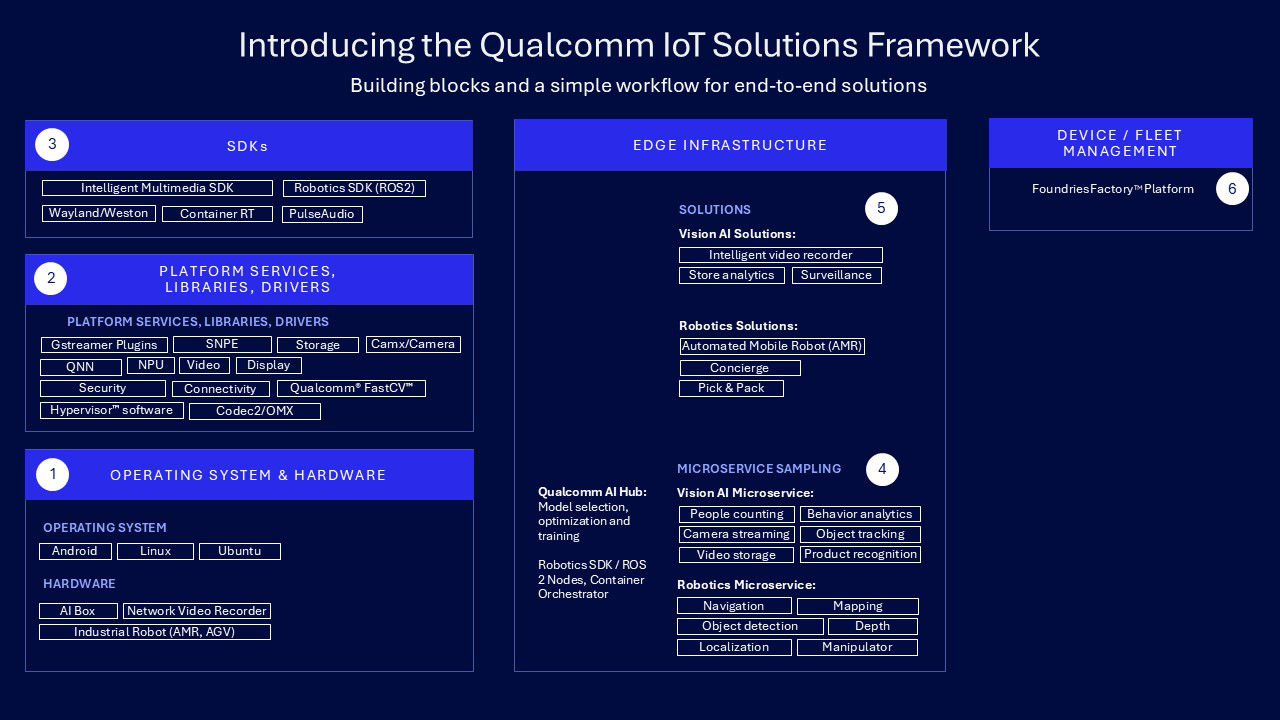
The Qualcomm IoT Solutions Framework represents a comprehensive suite of developer tools, reference blueprints and a robust ecosystem of partners
Qualcomm Technologies, Inc. is known for its vast collection of wireless-related intellectual property and its processor and components business. But we’ve widened our scope to begin creating unique Internet of Things (IoT) solutions that make the most of our technology.
We created the Qualcomm IoT Solutions Framework as a comprehensive suite of developer tools, reference blueprints and an ecosystem of partners that helps build solutions to the most daunting challenges facing industries. The goal is to help them easily develop end-to-end applications, successfully deploy and reduce the time to market.
For Qualcomm Technologies, it has meant looking past the chipset and leaning into helping customers solve business challenges and address specific needs.
Custom solutions made easy
Ecosystem partners, such as ISVs, developers, enterprises and industrial OEMs can use the library of microservices offered by Qualcomm Technologies as building blocks for a variety of uses, whether it’s enhancing video security and surveillance, drone services, industrial automation, worker assistance or more.
The team has made the process easier by creating a framework that allows developers and companies to build custom applications and solutions. The framework gives them an easy way to evaluate their performance on different platforms, allowing them to focus on the problems they’re solving. As a result, ecosystem partners benefit from apps and solutions that are developed quickly and effectively.
In our latest update, we’ve introduced several key features to enhance the application developer experience. We added support for Docker containers — including hardware acceleration for NPUs, GPUs, displays and VPUs in non-privileged mode — boosting security. Our microservices architecture improves scalability, flexibility and maintainability by breaking applications into smaller, independent services. We added Python bindings to let developers harness C++ performance with Python’s simplicity.
Additionally, we added daisy chain support to allow multiple artificial intelligence (AI) models to be linked in the same pipeline, expanding AI use cases. We also added Message Queuing Telemetry Transport (MQTT) support providing for efficient bandwidth usage, low power consumption and reliable communication. Also, we added E2E integration, model optimization and fine-tuning, which are now integrated with Qualcomm AI Hub. Lastly, the deployment process is streamlined with container infrastructure and Foundries.io integration.
This framework unifies all the core components that developers, ODMs and OEMs need to create tailored solutions. Early work focused on worker assistance, video surveillance and the use of drones in emergencies. Here’s a more in-depth look at some examples of end solutions built alongside Qualcomm Technologies.
Industrial worker assistance
Companies are keen to ensure their workers are as productive as possible, which means ensuring they have the right tools supporting them.
While working with ecosystem partners with specific needs, Qualcomm Technologies developed two solution types within the industrial worker assistance category.
The first was a way to give industrial workers the information they need to diagnose and repair equipment in the field.
This solution involved using either ruggedized handheld device or augmented reality glasses and pairing it with the right information. The combination of the AI-enabled camera in the device with Wi-Fi connectivity and on-device Edge Compute allowed workers of various skills to independently diagnose products.
As the camera takes in images of the equipment, AI models that have been fed a library of manuals, repair logs and product information can identify and offer appropriate responses. The system takes in multi-modal inputs, so a worker can ask the device a natural question like “Show me the repair history of this machine” and the system can deliver the right answer to the device or AR glasses.
The setup would include:
- Ruggedized handheld device or AR glasses with AI-enabled cameras.
- FoundriesFactory to manage devices, AI model deployment and data ingestion.
- Qualcomm Edge processors to manage AI modules, camera feeds and generative AI queries
The second solution involved saving worker time by giving them directions to materials found in a large warehouse. Qualcomm Technologies built a solution that mapped warehouse and product locations. It used cameras as sensors to scan a location and create a map with product or pallet locations, as well as directions to those areas.
Video surveillance and security
Another request was to add more intelligence of its existing video monitoring systems to support compliance with safety rules, like wearing hard hats or monitoring secure red zones. The problem was the company’s setup already employed “dumb” cameras.
These kinds of “brown field” deployments, where there’s older equipment, are common. Qualcomm Technologies presented a proof-of-concept solution that connected those cameras with edge boxes that allowed for AI computing on the premises. The camera data would flow back to a Qualcomm Command center.
Qualcomm Technologies then employed large language models (LLMs) to let the system comb through the footage to detect all instances of safety violations through product recognition and detection technology from Qualcomm Technologies. That saves someone from having to look at the hours of footage. An employee could use natural language for the system to generate reports on any specific incidents.
Here’s what the setup looked like:
- Qualcomm Edge AI Box Solutions connected to non-AI cameras, with additional AI cameras deployed as needed.
- Qualcomm AI-100-based on-prem compute to analyze events and enable LLM-based generative AI queries, alerts and reports.
- Generative AI Command Center that’s available for queries, snapshots, video feeds and reports and can accept conversational prompts.
Emergency and incident response
Qualcomm Technologies also created a system that triggers a drone to deploy at the first sign of a fire. Once the drone gets mission approval, it flies ahead of any first responders to the incident area.
The drone is programmed to determine the size of the fire and details like specific location and affected areas. It also immediately streams the video back to the incident center using cameras that work with the Qualcomm Drone Command Center. Qualcomm Technologies also set up a drone handover system that allows a fresh unit to take over if the first drones need a recharge.
The result is first responders getting AI-based situational awareness information well before they arrive on scene.
Here’s what the setup looks like:
- AI-based drones.
- On-prem compute, VMS and Flight Control, Drone Mission Control, Autonomous Flight Management and Video Streaming all managed on site.
- Dashcams and Bodycams feed into the integrated Mission Video Stream.
- Drone Command Center to manage drones, missions, video surveillance and generative AI flight controls.
These examples come from the different kinds of conversations Qualcomm Technologies is having with end customers. Every industry sector faces a multitude of business challenges and issues that require solutions.
While Qualcomm Technologies is renowned for our advanced technologies, our commitment goes much further. We’re committed to being a trusted advisor, assisting our partners in developing solutions to tackle these challenges. With the powerful and exciting potential of this framework approach, Qualcomm Technologies is set to greatly simplify the development, deployment and scaling of industrial IoT technologies from the edge to the cloud.
Suri Maddhula
VP, IoT Solutions Product Management, Qualcomm Technologies, Inc.