This blog post was originally published at TechNexion’s website. It is reprinted here with the permission of TechNexion.
3D scanning finds applications in multiple domains such as textile design, 3D printing, home remodeling, virtual reality, manufacturing, etc. Medical science hugely benefits from camera-enabled 3D scanning given that it is a non-invasive technique.
3D scanning is used in medical applications such as post-operative care, orthopedics, forensics, etc. While traditional scanning techniques come with the inability to account for the involuntary movement of the subject, stereo photogrammetry helps to capture a 3D image in a completely non-invasive manner.
Cameras play a huge role in the process of stereo photogrammetry by taking pictures from different angles – thereby helping to examine patients without exposing them to harmful radiation. In this article, let us learn how cameras and embedded vision are reimagining clinical care through the process of 3D stereo photogrammetry. We will explore how the process works, its benefits, and how cameras are a critical component of a 3D scanning system used in medical devices.
What is 3D Stereo Photogrammetry?
Photogrammetry is the process of obtaining measurements and other key information about an object by analyzing images and electromagnetic data. In the context of medical scanning, 3D stereo photogrammetry refers to using 2D images and depth information of the object to create a 3D model – which could be the entire human body or parts of it.
The term stereo refers to using two (or more) camera modules as stereo pairs to obtain images without using any invasive technique (unlike alternate technologies such as structured light). The dimensions of the object are then calculated with the help of stereo algorithms built into the photogrammetry software.
Benefits of 3D Stereo Photogrammetry

Using stereo photogrammetry for digital human modeling in medical treatment procedures offers the following benefits:
- 3D stereo photogrammetry is way less expensive compared to traditional scanning techniques. In addition, it offers high levels of accuracy for capturing non-static objects despite the involuntary movements of the subject.
- It doesn’t make use of any harmful radiation and hence is safer for use.
- It can capture a 360-degree view in one go without the subject having to move. This leads to improved accuracy by eliminating the possibility of errors caused due to the subject’s movement.
Applications of 3D Photogrammetry in Medical Treatment
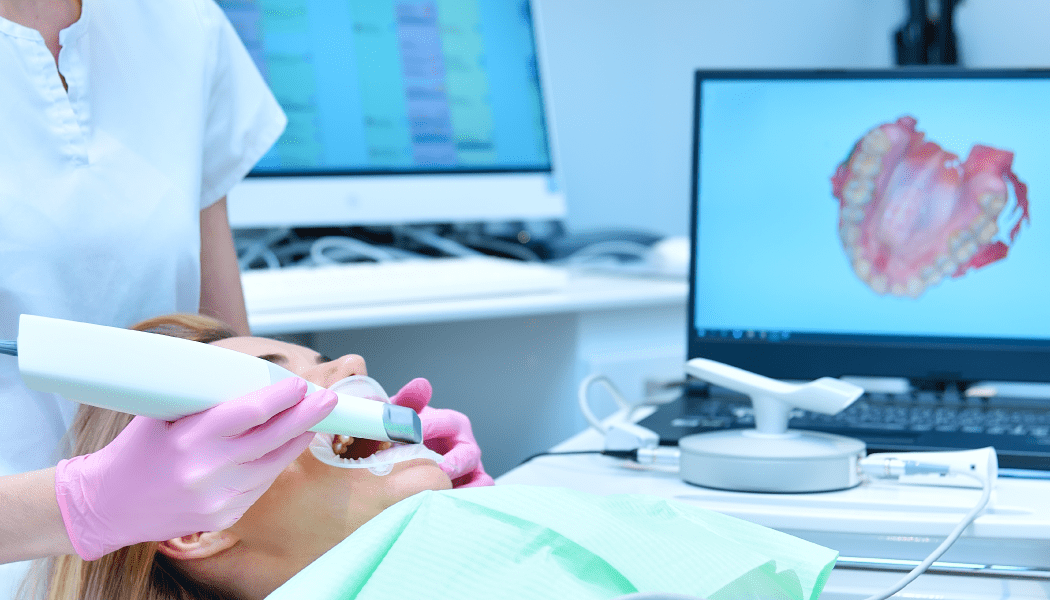
3D photogrammetry is used in medical tests that require a non-invasive examination of external or visible body parts (or the whole body) including hands, legs, head, or even teeth. Hence, it finds applications in the following areas:
- Orthopedic treatment: In orthopedics, 3D stereo photogrammetry will help to analyze fractures, deformations, and tears. This will help medical practitioners better assess the condition of the patient without having to be in contact with him or her.
- Orthodontics: The structure and shape of teeth can be effectively recreated using 3D photogrammetry. It can give the accurate texture and measurements of the subject’s teeth based on which the dentist can create effective treatment plans.
- Woundcare: Handheld wound measurement devices are in use that leverage camera modules to capture images of wounds. But they can only give two-dimensional output. On the other hand, multi-camera-based 3D scanning can give accurate three-dimensional measurements of the wound – leading to more accurate diagnosis and hence better care.
- Surgery and post-operative care: Multi-camera scanning can be used to assist non-invasive surgical procedures. This technique can also be used to assess the progress of the patient during the post-operative treatment window.
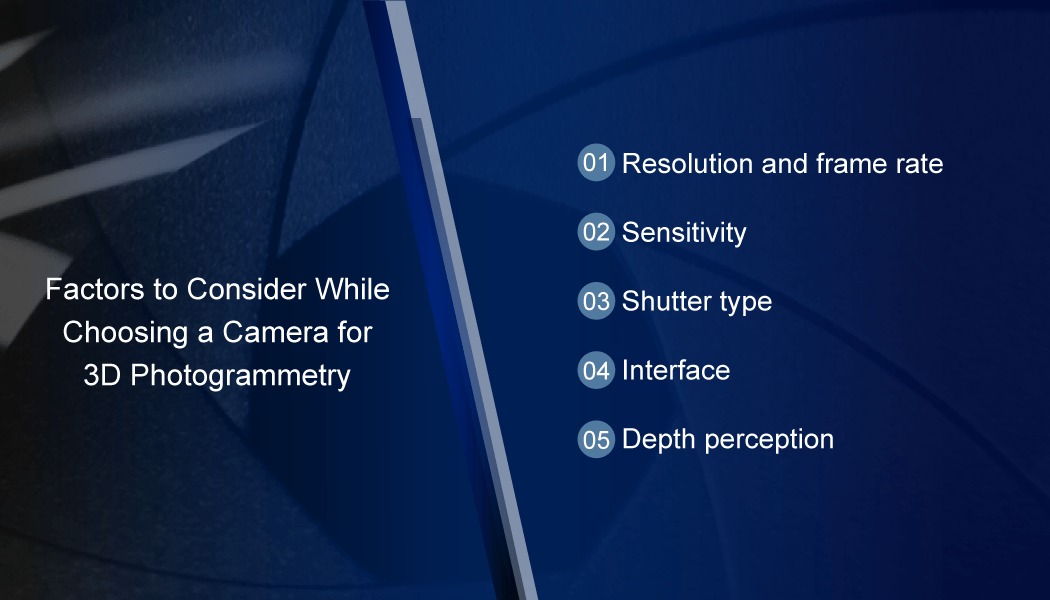
Factors You Need to Consider while Choosing a Camera for 3D Photogrammetry
The camera you choose heavily determines the quality of your 3D scanning system. The choice of lens matters too. To learn more about how to choose a lens for any application, please go through the following article: How to Choose Camera Lens for Embedded Vision Applications.
But here, let us delve into the details of the camera-related features you need to look at while evaluating a vision system for your 3D scanner.
- Resolution and frame rate: In most cases, a resolution of 3 to 4 MP is enough for 3D reconstruction. In peculiar cases where extremely high quality is a must, a resolution of 8MP or above can be chosen. When it comes to frame rate, since the subject is not moving fast, a frame rate of 30 fps or lower is sufficient. This will also allow you to go for higher resolutions with limited bandwidth if required.
- Sensitivity: It is recommended to go with a camera that comes with good sensitivity. Though 3D stereo photogrammetry typically uses flashlights, it is a good idea to account for low-light scenarios.
- Shutter type: A rolling shutter camera is more than enough for 3D scanning in medical applications since they don’t involve fast motion of the subject. Also read: Global Shutter vs. Rolling Shutter in Embedded Vision
- Interface: Depending on the nature of the scanning procedure, the size of the data to be transmitted will vary. 3D photogrammetry systems of the past involved using wireless SD cards installed on cameras for data transmission. However, modern 3D scanning systems use a wired interface for better reliability. The USB interface is a great choice in this case since the host system used is a PC. USB meets the bandwidth requirements of most 3D photogrammetry systems.
- Depth perception: scanning involves embedded cameras finding the exact location of the subject using depth data. In stereo photogrammetry, the vision system uses the stereo disparity technique to find the 3D coordinates of the subject. The accuracy of the depth data will depend on the quality of the camera as well as the stereo algorithm used to calculate depth. Since 3D scanning is done with a relatively large field of view, stereo is perfectly suited for the application.
Other Considerations while Integrating a Camera
In addition to the factors discussed in the previous section, there are a few things you need to keep in mind while integrating a camera into your photogrammetry-based 3D scanning device. These include:
- Camera and optics calibration: Camera and optics calibration helps to correct systematic errors caused by lens distortions and aberrations. This is a must-do process in a 3D photogrammetry system to achieve the desired level of accuracy. Two common methods of calibration used in these systems are Self Calibration (SC) and Full-Field Calibration (FFC).
- Buffer for on-camera storage: Some 3D scanning systems used in medical applications might have to transfer large files. Attempting to transfer them continuously might result in reliability issues. Having an onboard memory storage on the camera will help resolve the issue. This involves storing some data temporarily on the memory card and transferring it upon a trigger or instruction from the host.
- Multi-camera integration: 3D scanners are multi-camera systems. Hence, you need to factor in certain other parameters such as the number of cameras, synchronization method, image stitching, etc., while integrating embedded cameras into them.
To learn more about how multi-cameras are used in embedded vision and how to select one for an application, please read the following article: Multi-Camera Systems in Embedded Vision: Features and Applications.
To understand the differences between how a single camera and a multi-camera system operate, have a look at this article: Single Camera vs. Multi Camera – Similarities, Differences, and Applications.
3D Scanning in Medical Applications: What the Future Looks Like
Though 3D stereo photogrammetry is an effective low-cost solution for medical scanning, it does come with some limitations such as:
- Heavy processing load on the host system due to depth computation
- It has a limited depth range and might offer less accuracy at long distances compared to other depth technologies.
For these reasons, 3D scanning could see a higher adoption of other depth measurement techniques such as time of flight or structured light. They provide the depth information directly from the camera, unlike a stereo-based system. They offer relatively higher accuracy and do not add to the processing load of the host system. This further helps in improving the overall efficiency of the embedded vision system.
One key advantage of these alternatives that often go unnoticed is that they don’t involve the capturing of color images (unless the system uses an RGB camera). This safeguards the privacy of the subject by processing depth information alone.
Today, 3D photogrammetry is used in the medical industry primarily for scanning purposes. But here are a couple of newer use cases that could potentially use the technique in the future (or are at least experimenting with it):
- Rehabilitation: Rehabilitation procedures involve analyzing the mobility of the patient in various ways. 3D scanning can be used to automatically analyze these movements to accurately assess the progress of the patient.
- 3D bioprinting: 3D scanning using depth cameras is already used in the research and development of printing of organs. Though this is in a very early stage, scientists believe that this could soon be a reality. If it does, 3D camera technology will be a key component of the system.
TechNexion: Specialized Cameras for 3D Scanning

VLS3-AR0821-CB
TechNexion is an embedded solutions provider with a portfolio comprising embedded cameras, system modules, panel computing solutions, robotic solutions, etc. Of these, embedded cameras have been a focus area for us with medical being one of the key target applications.
Our cameras for medical devices are based on sensors such as AR0821, AR0521etc. Learn more about our embedded vision solutions here.


