|
Combining Flexibility and Low-Power in Embedded Vision Subsystems: An Application to Pedestrian Detection
Bruno Lavigueur, Embedded Vision Subsystem Project Leader at Synopsys, presents a case study of a pedestrian detection application. Starting from a high-level functional description in OpenCV, he decomposes and maps the application onto a heterogeneous platform consisting of a high-performance control processor and ASIPS (application-specific instruction-set processors). This application makes use of the HOG (Histogram of Oriented Gradients) algorithm. Lavigueur reviews the computation requirements of the different algorithm kernels, and presents possible mapping options onto the control processor and ASIPs. He also presents an OpenCV-to-ASIP software refinement methodology and supporting tools. He presents detailed results of the final configuration, consisting of one control processor and four ASIPs, including cost and power figures. Finally, he summarizes the results on an FPGA-based rapid prototyping platform.
Real-Time Traffic Sign Recognition on Mobile Processors
There is a growing need for fast and power-efficient computer vision on embedded devices. This session from NVIDIA's GTC (GPU Technology Conference) focuses on computer vision capabilities on embedded platforms available to ADAS developers, covering the OpenCV CUDA implementation and the computer vision standard, OpenVX. In addition, Itseez traffic sign detection is showcased. The algorithm is capable of detecting speed limit signs for both North America and EMEA regions as well as several other signs, delivering faster than real-time performance on an embedded platform with a mobile grade GPU.
More Videos
|
|
Deep Learning for Object Recognition: DSP and Specialized Processor Optimizations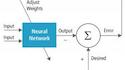
Neural networks enable the identification of objects in still and video images with impressive speed and accuracy after an initial training phase. This so-called "deep learning" has been enabled by the combination of the evolution of traditional neural network techniques, with one latest-incarnation example known as a CNN (convolutional neural network), by the steadily increasing processing "muscle" of CPUs aided by algorithm acceleration via various co-processors, by the steadily decreasing cost of system memory and storage, and by the wide availability of large and detailed data sets. In this collaborative article from the Alliance, co-authors (and Alliance member companies) Cadence, Movidius, NXP and Synopsys provide an overview of CNNs and then dive into optimization techniques for object recognition and other computer vision applications accelerated by DSPs and vision and CNN processors. More
Growth In the Global Professional Video Surveillance Market Slowed In 2015
The world market for professional video surveillance equipment grew by 1.9% in revenues in 2015. This is according to recently published estimates from IHS, through its Video Surveillance Intelligence Service. This is a much lower rate of growth than in 2014 (14.2%) and 2013 (6.8%). More
More Articles
|
|
A Brief Introduction to Deep Learning for Vision and the Caffe Framework: A Free Webinar from the Alliance: August 24, 2016
ARC Processor Summit: September 13, 2016, Santa Clara, California
Deep Learning for Vision Using CNNs and Caffe: A Hands-on Tutorial: September 22, 2016, Cambridge, Massachusetts
IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP): September 25-28, 2016, Phoenix, Arizona
SoftKinetic DepthSense Workshop: September 26-27, 2016, San Jose, California
Sensors Midwest (use code EVA for a free Expo pass): September 27-28, 2016, Rosemont, Illinois
Embedded Vision Summit: May 1-3, 2017, Santa Clara, California
More Events
|






