Development Tools for Embedded Vision
ENCOMPASSING MOST OF THE STANDARD ARSENAL USED FOR DEVELOPING REAL-TIME EMBEDDED PROCESSOR SYSTEMS
The software tools (compilers, debuggers, operating systems, libraries, etc.) encompass most of the standard arsenal used for developing real-time embedded processor systems, while adding in specialized vision libraries and possibly vendor-specific development tools for software development. On the hardware side, the requirements will depend on the application space, since the designer may need equipment for monitoring and testing real-time video data. Most of these hardware development tools are already used for other types of video system design.
Both general-purpose and vender-specific tools
Many vendors of vision devices use integrated CPUs that are based on the same instruction set (ARM, x86, etc), allowing a common set of development tools for software development. However, even though the base instruction set is the same, each CPU vendor integrates a different set of peripherals that have unique software interface requirements. In addition, most vendors accelerate the CPU with specialized computing devices (GPUs, DSPs, FPGAs, etc.) This extended CPU programming model requires a customized version of standard development tools. Most CPU vendors develop their own optimized software tool chain, while also working with 3rd-party software tool suppliers to make sure that the CPU components are broadly supported.
Heterogeneous software development in an integrated development environment
Since vision applications often require a mix of processing architectures, the development tools become more complicated and must handle multiple instruction sets and additional system debugging challenges. Most vendors provide a suite of tools that integrate development tasks into a single interface for the developer, simplifying software development and testing.
Exploring the COCO Dataset
This article was originally published at 3LC’s website. It is reprinted here with the permission of 3LC. The COCO dataset is a cornerstone of modern object detection, shaping models used in self-driving cars, robotics, and beyond. But what happens when we take a closer look? By examining annotations, embeddings, and dataset patterns at a granular
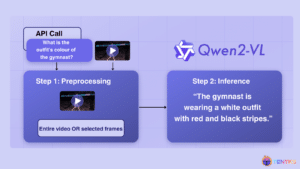
Video Understanding: Qwen2-VL, An Expert Vision-language Model
This article was originally published at Tenyks’ website. It is reprinted here with the permission of Tenyks. Qwen2-VL, an advanced vision language model built on Qwen2 [1], sets new benchmarks in image comprehension across varied resolutions and ratios, while also tackling extended video content. Though Qwen2-V excels at many fronts, this article explores the model’s

Powering IoT Developers with Edge AI: the Qualcomm RB3 Gen 2 Kit is Now Supported in the Edge Impulse Platform
This blog post was originally published at Qualcomm’s website. It is reprinted here with the permission of Qualcomm. The Qualcomm RB3 Gen 2 Development Kit has been designed to help you develop high-performance IoT and edge AI applications. With powerful AI acceleration, pre-validated peripherals, and extensive software support, this kit enables every engineer to move

Intel Accelerates AI at the Edge Through an Open Ecosystem
Intel empowers partners to seamlessly integrate AI into existing infrastructure with its new Intel AI Edge Systems, Edge AI Suites and Open Edge Platform software. What’s New: Intel is unveiling its new Intel® AI Edge Systems, Edge AI Suites and Open Edge Platform initiatives. These offerings help streamline and speed up AI adoption at the edge

NVIDIA Announces Isaac GR00T N1 — the World’s First Open Humanoid Robot Foundation Model — and Simulation Frameworks to Speed Robot Development
Now Available, Fully Customizable Foundation Model Brings Generalized Skills and Reasoning to Humanoid Robots NVIDIA, Google DeepMind and Disney Research Collaborate to Develop Next-Generation Open-Source Newton Physics Engine New Omniverse Blueprint for Synthetic Data Generation and Open-Source Dataset Jumpstart Physical AI Data Flywheel March 18, 2025—GTC—NVIDIA today announced a portfolio of technologies to supercharge humanoid

NVIDIA Announces Major Release of Cosmos World Foundation Models and Physical AI Data Tools
New Models Enable Prediction, Controllable World Generation and Reasoning for Physical AI Two New Blueprints Deliver Massive Physical AI Synthetic Data Generation for Robot and Autonomous Vehicle Post-Training 1X, Agility Robotics, Figure AI, Skild AI Among Early Adopters March 18, 2025—GTC—NVIDIA today announced a major release of new NVIDIA Cosmos™ world foundation models (WFMs), introducing

NVIDIA Unveils Open Physical AI Dataset to Advance Robotics and Autonomous Vehicle Development
Expected to become the world’s largest such dataset, the initial release of standardized synthetic data is now available to robotics developers as open source. Teaching autonomous robots and vehicles how to interact with the physical world requires vast amounts of high-quality data. To give researchers and developers a head start, NVIDIA is releasing a massive,

NVIDIA Announces DGX Spark and DGX Station Personal AI Computers
Powered by NVIDIA Grace Blackwell, Desktop Supercomputers Place Accelerated AI in the Hands of Developers, Researchers and Data Scientists; Systems Coming From Leading Computer Makers Including ASUS, Dell Technologies, HP and Lenovo March 18, 2025—GTC—NVIDIA today unveiled NVIDIA DGX™ personal AI supercomputers powered by the NVIDIA Grace Blackwell platform. DGX Spark — formerly Project DIGITS

