Processors for Embedded Vision
THIS TECHNOLOGY CATEGORY INCLUDES ANY DEVICE THAT EXECUTES VISION ALGORITHMS OR VISION SYSTEM CONTROL SOFTWARE
This technology category includes any device that executes vision algorithms or vision system control software. The following diagram shows a typical computer vision pipeline; processors are often optimized for the compute-intensive portions of the software workload.

The following examples represent distinctly different types of processor architectures for embedded vision, and each has advantages and trade-offs that depend on the workload. For this reason, many devices combine multiple processor types into a heterogeneous computing environment, often integrated into a single semiconductor component. In addition, a processor can be accelerated by dedicated hardware that improves performance on computer vision algorithms.
General-purpose CPUs
While computer vision algorithms can run on most general-purpose CPUs, desktop processors may not meet the design constraints of some systems. However, x86 processors and system boards can leverage the PC infrastructure for low-cost hardware and broadly-supported software development tools. Several Alliance Member companies also offer devices that integrate a RISC CPU core. A general-purpose CPU is best suited for heuristics, complex decision-making, network access, user interface, storage management, and overall control. A general purpose CPU may be paired with a vision-specialized device for better performance on pixel-level processing.
Graphics Processing Units
High-performance GPUs deliver massive amounts of parallel computing potential, and graphics processors can be used to accelerate the portions of the computer vision pipeline that perform parallel processing on pixel data. While General Purpose GPUs (GPGPUs) have primarily been used for high-performance computing (HPC), even mobile graphics processors and integrated graphics cores are gaining GPGPU capability—meeting the power constraints for a wider range of vision applications. In designs that require 3D processing in addition to embedded vision, a GPU will already be part of the system and can be used to assist a general-purpose CPU with many computer vision algorithms. Many examples exist of x86-based embedded systems with discrete GPGPUs.
Digital Signal Processors
DSPs are very efficient for processing streaming data, since the bus and memory architecture are optimized to process high-speed data as it traverses the system. This architecture makes DSPs an excellent solution for processing image pixel data as it streams from a sensor source. Many DSPs for vision have been enhanced with coprocessors that are optimized for processing video inputs and accelerating computer vision algorithms. The specialized nature of DSPs makes these devices inefficient for processing general-purpose software workloads, so DSPs are usually paired with a RISC processor to create a heterogeneous computing environment that offers the best of both worlds.
Field Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGAs)
Instead of incurring the high cost and long lead-times for a custom ASIC to accelerate computer vision systems, designers can implement an FPGA to offer a reprogrammable solution for hardware acceleration. With millions of programmable gates, hundreds of I/O pins, and compute performance in the trillions of multiply-accumulates/sec (tera-MACs), high-end FPGAs offer the potential for highest performance in a vision system. Unlike a CPU, which has to time-slice or multi-thread tasks as they compete for compute resources, an FPGA has the advantage of being able to simultaneously accelerate multiple portions of a computer vision pipeline. Since the parallel nature of FPGAs offers so much advantage for accelerating computer vision, many of the algorithms are available as optimized libraries from semiconductor vendors. These computer vision libraries also include preconfigured interface blocks for connecting to other vision devices, such as IP cameras.
Vision-Specific Processors and Cores
Application-specific standard products (ASSPs) are specialized, highly integrated chips tailored for specific applications or application sets. ASSPs may incorporate a CPU, or use a separate CPU chip. By virtue of their specialization, ASSPs for vision processing typically deliver superior cost- and energy-efficiency compared with other types of processing solutions. Among other techniques, ASSPs deliver this efficiency through the use of specialized coprocessors and accelerators. And, because ASSPs are by definition focused on a specific application, they are usually provided with extensive associated software. This same specialization, however, means that an ASSP designed for vision is typically not suitable for other applications. ASSPs’ unique architectures can also make programming them more difficult than with other kinds of processors; some ASSPs are not user-programmable.

PLP Technology Roadmap Toward High-end Packaging Fueled by AI
This market research report was originally published at the Yole Group’s website. It is reprinted here with the permission of the Yole Group. Yole Group anticipates strong growth in the PLP market with a 27% CAGR from 2024 to 2030, driven by its cost efficiency and ability to meet both advanced and traditional packaging needs.

High-performance AI In House: Qualcomm Dragonwing AI On-prem Appliance Solution and Qualcomm AI Inference Suite
This blog post was originally published at Qualcomm’s website. It is reprinted here with the permission of Qualcomm. The Qualcomm Dragonwing AI On-Prem Appliance Solution pairs with the software and services in the Qualcomm AI Inference Suite for AI inference that spans from near-edge to cloud. Together, they allow your small-to-medium business, enterprise or industrial
VeriSilicon Launches ISP9000: The Next-generation AI-embedded ISP for Intelligent Vision Applications
Deliver superior results in extremely low-light conditions, surpassing conventional computer vision technologies Shanghai, China, April 2, 2025–VeriSilicon (688521.SH) today unveiled its ISP9000 series Image Signal Processing (ISP) IP, a next-generation AI-embedded ISP solution designed to address the evolving demands of intelligent vision applications. Built on a flexible AI-optimized architecture, ISP9000 delivers exceptional image quality, low-latency

Qualcomm Expands Generative AI Capabilities With Acquisition of VinAI Division
Highlights: Acquisition will strengthen Qualcomm’s generative AI research and development capabilities and expedite the creation of advanced AI solutions for products like smartphones, PCs, software-defined vehicles, and more Dr. Hung Bui, VinAI’s founder and CEO, will join Qualcomm Apr 1, 2025 – SAN DIEGO & HANOI, VIETNAM – Qualcomm today announced the acquisition of MovianAI Artificial

BrainChip Partners with RTX’s Raytheon for AFRL Radar Contract
Laguna Hills, Calif. – April 1st, 2025 – BrainChip Holdings Ltd (ASX: BRN, OTCQX: BRCHF, ADR: BCHPY), the world’s first commercial producer of ultra-low power, fully digital, event-based, neuromorphic AI, today announced that it is partnering with Raytheon Company, an RTX (NYSE: RTX) business, to service a contract for $1.8M from the Air Force Research Laboratory

DeepSeek: Stop the Panic
DeepSeek is a precursor of many more disruptors coming in the AI world. Its importance may be overblown compared with what comes next. What’s at stake: DeepSeek nearly sank Nvidia and other AI model players. Except DeepSeek itself is barely known by anyone, its true story still a mystery, and the likely impact on the
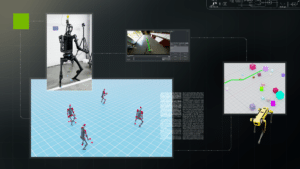
R²D²: Advancing Robot Mobility and Whole-body Control with Novel Workflows and AI Foundation Models from NVIDIA Research
This blog post was originally published at NVIDIA’s website. It is reprinted here with the permission of NVIDIA. Welcome to the first edition of the NVIDIA Robotics Research and Development Digest (R2D2). This technical blog series will give developers and researchers deeper insight and access to the latest physical AI and robotics research breakthroughs across

Sony Semiconductor Demonstration of AITRIOS Vision AI at the Extreme Edge Made Simple
Armaghan Ebrahimi, Senior Technical Product Manager, and Zachary Li, Product and Business Development Manager, both of Sony Semiconductor, demonstrates the company’s latest edge AI and vision technologies and products at the March 2025 Edge AI and Vision Alliance Forum. Specifically, Ebrahimi and Li demonstration the Raspberry Pi AI Camera, powered by Sony’s IMX500 smart sensor

Ambarella Debuts Next-generation Edge GenAI Technology at ISC West, Including Reasoning Models Running on its CVflow Edge AI SoCs
With Over 30 Million Edge AI Systems-on-Chip Shipped, Ambarella is Driving Innovation for a Broad Range of On-Device and On-Premise Generative AI Applications SANTA CLARA, Calif., March 31, 2025 — Ambarella, Inc. (NASDAQ: AMBA), an edge AI semiconductor company, today announced during the ISC West security expo that it is continuing to push the envelope

MemryX Raises $44 Million in Series B Funding for Advanced Edge AI Computing
ANN ARBOR, Mich., March 27, 2025 /PRNewswire/ — MemryX, a provider of industry leading Edge AI semiconductor solutions, announced today it has raised $44 million in Series B funding. The funding round received broad support from new and existing investors. This announcement follows MemryX reaching production quality of the industry leading MX3 Accelerator chip, the

OpenMV Demonstration of Its New N6 and AE3 Low Power Python Programmable AI Cameras and Other Products
Kwabena Agyeman, President and Co-founder of OpenMV, demonstrates the company’s latest edge AI and vision technologies and products at the March 2025 Edge AI and Vision Alliance Forum. Specifically, Agyeman demonstrates the company’s new N6 and AE3 low power Python programmable AI cameras, along with the FLIR BOSON thermal camera and Prophesee GENX320 event camera.
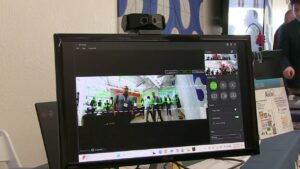
Andes Technology Demonstration of Its RISC-V IP in a Spherical Image Processor and Meta’s AI Accelerator
Marc Evans, Director of Business Development and Marketing at Andes Technology, demonstrates the company’s latest edge AI and vision technologies and products at the March 2025 Edge AI and Vision Alliance Forum. Specifically, Evans demonstrates the company’s RISC-V semiconductor processor IP, which enables customers to develop leading SoCs for AI, computer vision and other market

RGo Robotics Implements Vision-based Perception Engine on Qualcomm SoCs for Robotics Market
This blog post was originally published at Qualcomm’s website. It is reprinted here with the permission of Qualcomm. Mobile robotics developers equip their machines to behave autonomously in the real world by generating facility maps, localizing within them and understanding the geometry of their surroundings. Machines like autonomous mobile robots (AMR), automated guided vehicles (AGV)
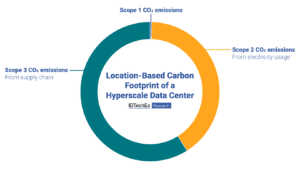
Key Insights from Data Centre World 2025: Sustainability and AI
Scope 2 power-based emissions and Scope 3 supply chain emissions make the biggest contribution to the data center’s carbon footprint. IDTechEx’s Sustainability for Data Centers report explores which technologies can reduce these emissions. Major data center players converged in London, UK, in the middle of March for the 2025 iteration of Data Centre World. Co-located
Explaining Tokens — The Language and Currency of AI
This blog post was originally published at NVIDIA’s website. It is reprinted here with the permission of NVIDIA. Under the hood of every AI application are algorithms that churn through data in their own language, one based on a vocabulary of tokens. Tokens are tiny units of data that come from breaking down bigger chunks

Upcoming In-person Event from Andes Technology Explores the RISC-V Ecosystem
On April 29, 2025 from 9:00 AM to 6:00 PM PT, Alliance Member company Andes Technology will deliver the RISC-V CON Silicon Valley event at the DoubleTree Hotel by Hilton in San Jose, CA. Jeff Bier, Founder of the Edge AI and Vision Alliance, will be one of the invited guest speakers. From the event
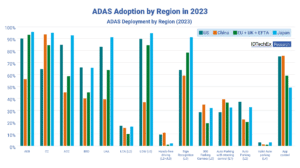
L2+ ADAS Outpaces L3 in Europe, US$4B by 2042
14 ADAS Features Deployed in EU. Privately owned Level 3 autonomous vehicles encountered significant regulatory setbacks in 2017 when Audi attempted to pioneer the market with the L3-ready A8. Regulatory uncertainty quickly stalled these ambitions, delaying the introduction of true L3 autonomy. By 2021, a clearer regulatory framework emerged under UNECE guidelines, affecting Europe and

Powering IoT Developers with Edge AI: the Qualcomm RB3 Gen 2 Kit is Now Supported in the Edge Impulse Platform
This blog post was originally published at Qualcomm’s website. It is reprinted here with the permission of Qualcomm. The Qualcomm RB3 Gen 2 Development Kit has been designed to help you develop high-performance IoT and edge AI applications. With powerful AI acceleration, pre-validated peripherals, and extensive software support, this kit enables every engineer to move

Intel Accelerates AI at the Edge Through an Open Ecosystem
Intel empowers partners to seamlessly integrate AI into existing infrastructure with its new Intel AI Edge Systems, Edge AI Suites and Open Edge Platform software. What’s New: Intel is unveiling its new Intel® AI Edge Systems, Edge AI Suites and Open Edge Platform initiatives. These offerings help streamline and speed up AI adoption at the edge

NVIDIA Announces Isaac GR00T N1 — the World’s First Open Humanoid Robot Foundation Model — and Simulation Frameworks to Speed Robot Development
Now Available, Fully Customizable Foundation Model Brings Generalized Skills and Reasoning to Humanoid Robots NVIDIA, Google DeepMind and Disney Research Collaborate to Develop Next-Generation Open-Source Newton Physics Engine New Omniverse Blueprint for Synthetic Data Generation and Open-Source Dataset Jumpstart Physical AI Data Flywheel March 18, 2025—GTC—NVIDIA today announced a portfolio of technologies to supercharge humanoid

