Processors for Embedded Vision
THIS TECHNOLOGY CATEGORY INCLUDES ANY DEVICE THAT EXECUTES VISION ALGORITHMS OR VISION SYSTEM CONTROL SOFTWARE
This technology category includes any device that executes vision algorithms or vision system control software. The following diagram shows a typical computer vision pipeline; processors are often optimized for the compute-intensive portions of the software workload.

The following examples represent distinctly different types of processor architectures for embedded vision, and each has advantages and trade-offs that depend on the workload. For this reason, many devices combine multiple processor types into a heterogeneous computing environment, often integrated into a single semiconductor component. In addition, a processor can be accelerated by dedicated hardware that improves performance on computer vision algorithms.
General-purpose CPUs
While computer vision algorithms can run on most general-purpose CPUs, desktop processors may not meet the design constraints of some systems. However, x86 processors and system boards can leverage the PC infrastructure for low-cost hardware and broadly-supported software development tools. Several Alliance Member companies also offer devices that integrate a RISC CPU core. A general-purpose CPU is best suited for heuristics, complex decision-making, network access, user interface, storage management, and overall control. A general purpose CPU may be paired with a vision-specialized device for better performance on pixel-level processing.
Graphics Processing Units
High-performance GPUs deliver massive amounts of parallel computing potential, and graphics processors can be used to accelerate the portions of the computer vision pipeline that perform parallel processing on pixel data. While General Purpose GPUs (GPGPUs) have primarily been used for high-performance computing (HPC), even mobile graphics processors and integrated graphics cores are gaining GPGPU capability—meeting the power constraints for a wider range of vision applications. In designs that require 3D processing in addition to embedded vision, a GPU will already be part of the system and can be used to assist a general-purpose CPU with many computer vision algorithms. Many examples exist of x86-based embedded systems with discrete GPGPUs.
Digital Signal Processors
DSPs are very efficient for processing streaming data, since the bus and memory architecture are optimized to process high-speed data as it traverses the system. This architecture makes DSPs an excellent solution for processing image pixel data as it streams from a sensor source. Many DSPs for vision have been enhanced with coprocessors that are optimized for processing video inputs and accelerating computer vision algorithms. The specialized nature of DSPs makes these devices inefficient for processing general-purpose software workloads, so DSPs are usually paired with a RISC processor to create a heterogeneous computing environment that offers the best of both worlds.
Field Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGAs)
Instead of incurring the high cost and long lead-times for a custom ASIC to accelerate computer vision systems, designers can implement an FPGA to offer a reprogrammable solution for hardware acceleration. With millions of programmable gates, hundreds of I/O pins, and compute performance in the trillions of multiply-accumulates/sec (tera-MACs), high-end FPGAs offer the potential for highest performance in a vision system. Unlike a CPU, which has to time-slice or multi-thread tasks as they compete for compute resources, an FPGA has the advantage of being able to simultaneously accelerate multiple portions of a computer vision pipeline. Since the parallel nature of FPGAs offers so much advantage for accelerating computer vision, many of the algorithms are available as optimized libraries from semiconductor vendors. These computer vision libraries also include preconfigured interface blocks for connecting to other vision devices, such as IP cameras.
Vision-Specific Processors and Cores
Application-specific standard products (ASSPs) are specialized, highly integrated chips tailored for specific applications or application sets. ASSPs may incorporate a CPU, or use a separate CPU chip. By virtue of their specialization, ASSPs for vision processing typically deliver superior cost- and energy-efficiency compared with other types of processing solutions. Among other techniques, ASSPs deliver this efficiency through the use of specialized coprocessors and accelerators. And, because ASSPs are by definition focused on a specific application, they are usually provided with extensive associated software. This same specialization, however, means that an ASSP designed for vision is typically not suitable for other applications. ASSPs’ unique architectures can also make programming them more difficult than with other kinds of processors; some ASSPs are not user-programmable.

Customize e-con Systems’ FPGA IP Cores to Meet Unique Vision Needs
This blog post was originally published at e-con Systems’ website. It is reprinted here with the permission of e-con Systems. Developing cutting-edge vision systems requires more than just advanced hardware—it demands the ability to customize and optimize image processing to meet specific application needs. That’s why e-con Systems offers a suite of high-performance Image Signal

NVIDIA DRIVE Hyperion Platform Achieves Critical Automotive Safety and Cybersecurity Milestones for AV Development
Adopted and Backed by Automotive Manufacturers and Safety Authorities, Latest Iteration to Feature DRIVE Thor on NVIDIA Blackwell Running NVIDIA DriveOS January 6, 2025 — CES — NVIDIA today announced that its autonomous vehicle (AV) platform, NVIDIA DRIVE AGX™ Hyperion, has passed industry-safety assessments by TÜV SÜD and TÜV Rheinland — two of the industry’s
NVIDIA Expands Omniverse With Generative Physical AI
New Models, Including Cosmos World Foundation Models, and Omniverse Mega Factory and Robotic Digital Twin Blueprint Lay the Foundation for Industrial AI Leading Developers Accenture, Altair, Ansys, Cadence, Microsoft and Siemens Among First to Adopt Platform Libraries January 6, 2025 — CES — NVIDIA today announced generative AI models and blueprints that expand NVIDIA Omniverse™

BrainChip Unveils Edge AI Box Partner Ecosystem for Gestures, Cybersecurity, Image Recognition, and Computer Vision
Laguna Hills, Calif. – January 7th, 2025 – BrainChip Holdings Ltd (ASX: BRN, OTCQX: BRCHF, ADR: BCHPY), the world’s first commercial producer of ultra-low power, fully digital, event-based, brain-inspired AI, today announced an all-star lineup of partners developing revolutionary technology demonstrations and products with the Akida™ Edge AI Box, a compact, cost-effective appliance with AI/ML
VeriSilicon’s Display Processing IP DC8200-FS Has Achieved ISO 26262 ASIL B Certification
Empowering smarter, safer automotive displays with advanced performance Las Vegas, USA, January 7, 2025–VeriSilicon (688521.SH) today announced that its high-performance, low-power Display Processing IP DC8200-FS has successfully achieved ISO 26262 ASIL B automotive functional safety certification. The certificate was issued by TÜV NORD, an international inspection and certification institution. Fully compliant with ISO 26262 ASIL

NVIDIA Launches Cosmos World Foundation Model Platform to Accelerate Physical AI Development
New State-of-the-Art Models, Video Tokenizers and an Accelerated Data Processing Pipeline, Optimized for NVIDIA Data Center GPUs, Are Purpose-Built for Developing Robots and Autonomous Vehicles First Wave of Open Models Available Now to Developer Community Global Physical AI Leaders 1X, Agile Robots, Agility, Figure AI, Foretellix, Uber, Waabi and XPENG Among First to Adopt January 6, 2025 —

NVIDIA Launches AI Foundation Models for RTX AI PCs
NVIDIA NIM Microservices and AI Blueprints Help Developers and Enthusiasts Build AI Agents and Creative Workflows on PC January 6, 2025 — CES — NVIDIA today announced foundation models running locally on NVIDIA RTX™ AI PCs that supercharge digital humans, content creation, productivity and development. These models — offered as NVIDIA NIM™ microservices — are accelerated by

NVIDIA Puts Grace Blackwell on Every Desk and at Every AI Developer’s Fingertips
NVIDIA Project DIGITS With New GB10 Superchip Debuts as World’s Smallest AI Supercomputer Capable of Running 200B-Parameter Models January 6, 2025 — CES — NVIDIA today unveiled NVIDIA® Project DIGITS, a personal AI supercomputer that provides AI researchers, data scientists and students worldwide with access to the power of the NVIDIA Grace Blackwell platform. Project

NXP Accelerates the Transformation to Software-defined Vehicles (SDV) with Agreement to Acquire TTTech Auto
NXP strengthens its automotive business with a leading software solution provider specialized in the systems, safety and security required for SDVs TTTech Auto complements and accelerates the NXP CoreRide platform, enabling automakers to reduce complexity, maximize system performance and shorten time to market The acquisition is the next milestone in NXP’s strategy to be the

Optimizing Multimodal AI Inference
This blog post was originally published at Intel’s website. It is reprinted here with the permission of Intel. Multimodal models are becoming essential for AI, enabling the integration of diverse data types into a single model for richer insights. During the second Intel® Liftoff Days 2024 hackathon, Rahul Nair’s workshop on Inference of Multimodal Models

NVIDIA Blackwell GeForce RTX 50 Series Opens New World of AI Computer Graphics
Next Generation of GeForce RTX GPUs Deliver Stunning Visual Realism and 2x Performance Increase, Made Possible by AI, Neural Shaders and DLSS 4 January 6, 2025 — CES — NVIDIA today unveiled the most advanced consumer GPUs for gamers, creators and developers — the GeForce RTX™ 50 Series Desktop and Laptop GPUs. Powered by the

Qualcomm Brings Industry-leading AI Innovations and Broad Collaborations to CES 2025 Across PC, Automotive, Smart Home and Enterprises
Highlights: Spotlight on bringing edge AI across devices and computing spaces, including PC, automotive, smart home and into enterprises broadly, with global ecosystem partners at the show. In PC, continued traction for the Snapdragon X Series, the launch of the new Snapdragon X platform, and the launch of a new desktop form factor and NPU-powered

Qualcomm Aware Unveils New Services to Drive Connected Intelligence Across Industries
Highlights: Qualcomm Aware adds observability, monitoring and location services to enable the development of IoT solutions that meet specific needs and challenges of consumers and enterprises across a wide range of industries and use cases. By pre-integrating Qualcomm Aware software across select Qualcomm Technologies and third-party processors, Qualcomm Technologies will provide a simple, fast and

Snapdragon X Series Continues to Redefine the PC Category with a New Platform, Mini Desktop Form Factors, and NPU Powered AI Experiences
Highlights: The 4th platform to join the Snapdragon X Series, Snapdragon X, brings AI PC leadership to Copilot+ PCs in the $600 range. Snapdragon X Series continues to gain traction with now over 60 designs in production or development with more than 100 coming by 2026 from leading OEMs including Asus, Acer, Dell Technologies, HP,

AMD Announces Expanded Consumer and Commercial AI PC Portfolio at CES
AMD Ryzen™ AI Max, AMD Ryzen™ AI 300 Series and AMD Ryzen™ 200 Series processors bring incredible performance for next-gen AI PCs AMD Ryzen™ AI Max PRO, AMD Ryzen™ AI 300 PRO and AMD Ryzen™ 200 PRO Series processors bring cutting-edge performance to business PCs LAS VEGAS, Jan. 06, 2025 (GLOBE NEWSWIRE) — AMD (NASDAQ:

Qualcomm Launches On-prem AI Appliance Solution and Inference Suite to Step-up AI Inference Privacy, Flexibility and Cost Savings Across Enterprise and Industrial Verticals
Highlights: Qualcomm AI On-Prem Appliance Solution is designed for generative AI inference and computer vision workloads on dedicated on-premises hardware – allowing sensitive customer data, fine-tuned models, and inference loads to remain on premises. Qualcomm AI Inference Suite provides ready-to-use AI applications and agents, tools and libraries for operationalizing AI from computer vision to generative

Axelera AI at CES: Honored to Showcase Innovation at the Edge
Axelera AI is thrilled to join the global innovation of CES 2025, where the spotlight will shine on our cutting-edge Metis product line and its ability to redefine AI inference at the edge. Our fully integrated hardware/software solutions deliver unparalleled performance, energy efficiency, and adaptability to a wide range of applications, all while protecting your

Intel Extends Leadership in AI PCs and Edge Computing at CES 2025
Intel pushes the boundaries of AI performance and power efficiency for businesses and consumers, ushering in the next era of AI computing. News Highlights New Intel® Core™ Ultra 200V series mobile processors with Intel vPro® are empowering businesses with AI-driven productivity and enhanced IT management1. The combination of performance, efficiency and industry-leading business computing with
Chiplet Technology: Unlocking New Potential in the Semiconductor Industry
In the rapidly evolving semiconductor industry, chiplet technology is emerging as a transformative force, offering innovative solutions to many of the challenges faced by traditional monolithic System-on-Chip (SoC) designs. As highlighted in the IDTechEx report, “Chiplet Technology 2025-2035: Technology, Opportunities, Applications,” this modular approach not only enhances performance and functionality but also opens up a
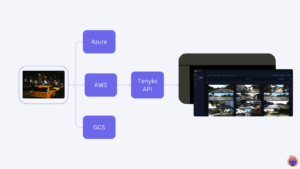
NVIDIA TAO Toolkit: How to Build a Data-centric Pipeline to Improve Model Performance (Part 2 of 3)
This blog post was originally published at Tenyks’ website. It is reprinted here with the permission of Tenyks. During this series, we will use Tenyks to build a data-centric pipeline to debug and fix a model trained with the NVIDIA TAO Toolkit. Part 1. We demystify the NVIDIA ecosystem and define a data-centric pipeline based

