Vision Algorithms for Embedded Vision
Most computer vision algorithms were developed on general-purpose computer systems with software written in a high-level language
Most computer vision algorithms were developed on general-purpose computer systems with software written in a high-level language. Some of the pixel-processing operations (ex: spatial filtering) have changed very little in the decades since they were first implemented on mainframes. With today’s broader embedded vision implementations, existing high-level algorithms may not fit within the system constraints, requiring new innovation to achieve the desired results.
Some of this innovation may involve replacing a general-purpose algorithm with a hardware-optimized equivalent. With such a broad range of processors for embedded vision, algorithm analysis will likely focus on ways to maximize pixel-level processing within system constraints.
This section refers to both general-purpose operations (ex: edge detection) and hardware-optimized versions (ex: parallel adaptive filtering in an FPGA). Many sources exist for general-purpose algorithms. The Embedded Vision Alliance is one of the best industry resources for learning about algorithms that map to specific hardware, since Alliance Members will share this information directly with the vision community.
General-purpose computer vision algorithms
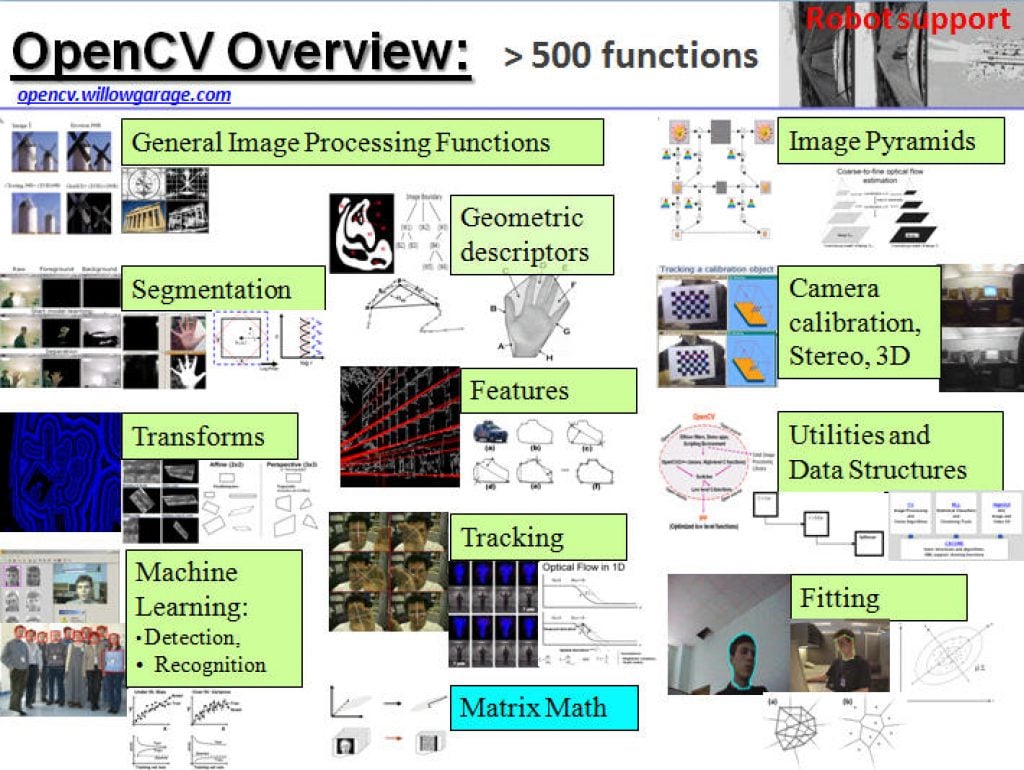
One of the most-popular sources of computer vision algorithms is the OpenCV Library. OpenCV is open-source and currently written in C, with a C++ version under development. For more information, see the Alliance’s interview with OpenCV Foundation President and CEO Gary Bradski, along with other OpenCV-related materials on the Alliance website.
Hardware-optimized computer vision algorithms
Several programmable device vendors have created optimized versions of off-the-shelf computer vision libraries. NVIDIA works closely with the OpenCV community, for example, and has created algorithms that are accelerated by GPGPUs. MathWorks provides MATLAB functions/objects and Simulink blocks for many computer vision algorithms within its Vision System Toolbox, while also allowing vendors to create their own libraries of functions that are optimized for a specific programmable architecture. National Instruments offers its LabView Vision module library. And Xilinx is another example of a vendor with an optimized computer vision library that it provides to customers as Plug and Play IP cores for creating hardware-accelerated vision algorithms in an FPGA.
Other vision libraries
- Halcon
- Matrox Imaging Library (MIL)
- Cognex VisionPro
- VXL
- CImg
- Filters

Intel Accelerates AI at the Edge Through an Open Ecosystem
Intel empowers partners to seamlessly integrate AI into existing infrastructure with its new Intel AI Edge Systems, Edge AI Suites and Open Edge Platform software. What’s New: Intel is unveiling its new Intel® AI Edge Systems, Edge AI Suites and Open Edge Platform initiatives. These offerings help streamline and speed up AI adoption at the edge

NVIDIA Announces Isaac GR00T N1 — the World’s First Open Humanoid Robot Foundation Model — and Simulation Frameworks to Speed Robot Development
Now Available, Fully Customizable Foundation Model Brings Generalized Skills and Reasoning to Humanoid Robots NVIDIA, Google DeepMind and Disney Research Collaborate to Develop Next-Generation Open-Source Newton Physics Engine New Omniverse Blueprint for Synthetic Data Generation and Open-Source Dataset Jumpstart Physical AI Data Flywheel March 18, 2025—GTC—NVIDIA today announced a portfolio of technologies to supercharge humanoid

NVIDIA Announces Major Release of Cosmos World Foundation Models and Physical AI Data Tools
New Models Enable Prediction, Controllable World Generation and Reasoning for Physical AI Two New Blueprints Deliver Massive Physical AI Synthetic Data Generation for Robot and Autonomous Vehicle Post-Training 1X, Agility Robotics, Figure AI, Skild AI Among Early Adopters March 18, 2025—GTC—NVIDIA today announced a major release of new NVIDIA Cosmos™ world foundation models (WFMs), introducing

NVIDIA Unveils Open Physical AI Dataset to Advance Robotics and Autonomous Vehicle Development
Expected to become the world’s largest such dataset, the initial release of standardized synthetic data is now available to robotics developers as open source. Teaching autonomous robots and vehicles how to interact with the physical world requires vast amounts of high-quality data. To give researchers and developers a head start, NVIDIA is releasing a massive,

Build Real-time Multimodal XR Apps with NVIDIA AI Blueprint for Video Search and Summarization
This article was originally published at NVIDIA’s website. It is reprinted here with the permission of NVIDIA. With the recent advancements in generative AI and vision foundational models, VLMs present a new wave of visual computing wherein the models are capable of highly sophisticated perception and deep contextual understanding. These intelligent solutions offer a promising

OpenMV Unveils the N6 and AE3: High-performance, Low-power AI Vision Cameras for Makers and Professionals
March 17, 2025, San Francisco, CA – OpenMV is excited to announce the launch of the OpenMV N6 and OpenMV AE3, two groundbreaking machine vision cameras designed to bring real-time AI capabilities to microcontrollers. Backed by years of expertise in embedded vision, OpenMV is making high-performance AI vision accessible to developers, researchers, and hobbyists alike

Navigating the AI Implementation Journey: Buy or Build?
This blog post was originally published at Tryolabs’ website. It is reprinted here with the permission of Tryolabs. Many companies waste millions of dollars and critical time-to-market because they make the wrong decision on a seemingly simple question: should you buy an off-the-shelf AI solution or build your own? If you’re an AI project owner

Optimizing Edge AI for Effective Real-time Decision Making in Robotics
This blog post was originally published at Geisel Software’s website. It is reprinted here with the permission of Geisel Software. Optimizing Edge AI Key Takeaways Instant Decisions, Real-World Impact: Edge AI empowers robots to react in milliseconds, enabling life-saving actions in critical scenarios like autonomous vehicle collision avoidance and rapid search-and-rescue missions. Unshakeable Reliability, Unbreachable
Scalable Video Search: Cascading Foundation Models
This article was originally published at Tenyks’ website. It is reprinted here with the permission of Tenyks. Video has become the lingua franca of the digital age, but its ubiquity presents a unique challenge: how do we efficiently extract meaningful information from this ocean of visual data? In Part 1 of this series, we navigate

Passenger Car ADAS Market 2025-2045: Technology, Market Analysis, and Forecasts
For more information, visit https://www.idtechex.com/en/research-report/passenger-car-adas-market-2025-2045-technology-market-analysis-and-forecasts/1080. Global L2+/L3 feature adoption will exceed 50% by 2035. Over the past few years, Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) have become a core competitive factor in the passenger vehicles market. In particular, “Level 2+” has emerged as a term describing advanced Level 2 ADAS with more sophisticated capabilities, such as
Building a Simple VLM-based Multimodal Information Retrieval System with NVIDIA NIM
This article was originally published at NVIDIA’s website. It is reprinted here with the permission of NVIDIA. In today’s data-driven world, the ability to retrieve accurate information from even modest amounts of data is vital for developers seeking streamlined, effective solutions for quick deployments, prototyping, or experimentation. One of the key challenges in information retrieval
Productionizing State-of-the-art Models at the Edge for Smart City Use Cases (Part I)
This blog post was originally published at CLIKA’s website. It is reprinted here with the permission of CLIKA. Approaches to productionizing models for edge applications can vary greatly depending on user priorities, with some models not requiring model optimization at all. An organization can choose pre-existing models designed specifically for edge use cases with performance
Qualcomm at Embedded World: Accelerating Digital Transformation with Edge AI
This blog post was originally published at Qualcomm’s website. It is reprinted here with the permission of Qualcomm. An essential partner to the embedded community, Qualcomm Technologies, Inc. strengthens its leadership in intelligent computing with several key announcements The AI revolution is sparking a wave of innovation in the embedded community, spawning a flurry of

AutoML Decoded: The Ultimate Guide and Tools Comparison
This article was originally published at Tryolabs’ website. It is reprinted here with the permission of Tryolabs. The quest for efficient and user-friendly solutions has led to the emergence of a game-changing concept: Automated Machine Learning (AutoML). AutoML is the process of automating the tasks involved in the entire Machine Learning lifecycle, such as data
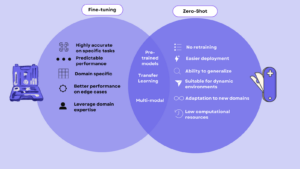
Zero-Shot AI: The End of Fine-tuning as We Know It?
This article was originally published at Tenyks’ website. It is reprinted here with the permission of Tenyks. Models like SAM 2, LLaVA or ChatGPT can do tasks without special training. This has people wondering if the old way (i.e., fine-tuning) of training AI is becoming outdated. In this article, we compare two models: YOLOv8 (fine-tuning)

3LC: What is It and Who is It For?
This blog post was originally published at 3LC’s website. It is reprinted here with the permission of 3LC. AI performance isn’t just about better architectures or more compute – it’s about better data. Even perfectly labeled datasets can hold hidden inefficiencies that limit accuracy. See how teams use 3LC to refine datasets, optimize labeling strategies,

