Vision Algorithms for Embedded Vision
Most computer vision algorithms were developed on general-purpose computer systems with software written in a high-level language
Most computer vision algorithms were developed on general-purpose computer systems with software written in a high-level language. Some of the pixel-processing operations (ex: spatial filtering) have changed very little in the decades since they were first implemented on mainframes. With today’s broader embedded vision implementations, existing high-level algorithms may not fit within the system constraints, requiring new innovation to achieve the desired results.
Some of this innovation may involve replacing a general-purpose algorithm with a hardware-optimized equivalent. With such a broad range of processors for embedded vision, algorithm analysis will likely focus on ways to maximize pixel-level processing within system constraints.
This section refers to both general-purpose operations (ex: edge detection) and hardware-optimized versions (ex: parallel adaptive filtering in an FPGA). Many sources exist for general-purpose algorithms. The Embedded Vision Alliance is one of the best industry resources for learning about algorithms that map to specific hardware, since Alliance Members will share this information directly with the vision community.
General-purpose computer vision algorithms
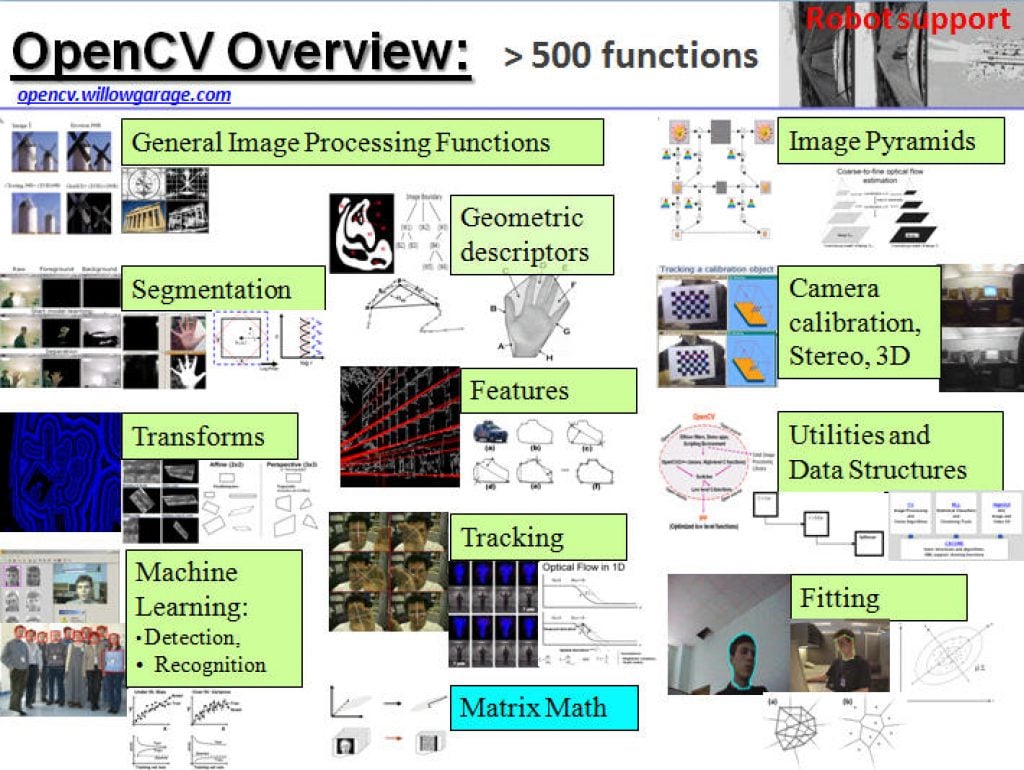
One of the most-popular sources of computer vision algorithms is the OpenCV Library. OpenCV is open-source and currently written in C, with a C++ version under development. For more information, see the Alliance’s interview with OpenCV Foundation President and CEO Gary Bradski, along with other OpenCV-related materials on the Alliance website.
Hardware-optimized computer vision algorithms
Several programmable device vendors have created optimized versions of off-the-shelf computer vision libraries. NVIDIA works closely with the OpenCV community, for example, and has created algorithms that are accelerated by GPGPUs. MathWorks provides MATLAB functions/objects and Simulink blocks for many computer vision algorithms within its Vision System Toolbox, while also allowing vendors to create their own libraries of functions that are optimized for a specific programmable architecture. National Instruments offers its LabView Vision module library. And Xilinx is another example of a vendor with an optimized computer vision library that it provides to customers as Plug and Play IP cores for creating hardware-accelerated vision algorithms in an FPGA.
Other vision libraries
- Halcon
- Matrox Imaging Library (MIL)
- Cognex VisionPro
- VXL
- CImg
- Filters

3LC: What is It and Who is It For?
This blog post was originally published at 3LC’s website. It is reprinted here with the permission of 3LC. AI performance isn’t just about better architectures or more compute – it’s about better data. Even perfectly labeled datasets can hold hidden inefficiencies that limit accuracy. See how teams use 3LC to refine datasets, optimize labeling strategies,

How e-con Systems’ TintE ISP IP Core Increases the Efficiency of Embedded Vision Applications
This blog post was originally published at e-con Systems’ website. It is reprinted here with the permission of e-con Systems. e-con Systems has developed TintE™, a ready to deploy ISP IP core engineered to enhance image quality in camera systems. Built to deliver high performance on leading FPGA platforms, it accelerates real-time image processing with

Vision Language Model Prompt Engineering Guide for Image and Video Understanding
This blog post was originally published at NVIDIA’s website. It is reprinted here with the permission of NVIDIA. Vision language models (VLMs) are evolving at a breakneck speed. In 2020, the first VLMs revolutionized the generative AI landscape by bringing visual understanding to large language models (LLMs) through the use of a vision encoder. These

Fine-tuning LLMs for Cost-effective GenAI Inference at Scale
This article was originally published at Tryolabs’ website. It is reprinted here with the permission of Tryolabs. Data is the new oil, fueling the AI revolution. From user-tailored shopping assistants to AI researchers, to recreating the King, the applicability of AI models knows no bounds. Yet these models are only as good as the data

SAM 2 + GPT-4o: Cascading Foundation Models via Visual Prompting (Part 2)
This article was originally published at Tenyks’ website. It is reprinted here with the permission of Tenyks. In Part 2 of our Segment Anything Model 2 (SAM 2) Series, we show how foundation models (e.g., GPT-4o, Claude Sonnet 3.5 and YOLO-World) can be used to generate visual inputs (e.g., bounding boxes) for SAM 2. Learn

Taming LLMs: Strategies and Tools for Controlling Responses
This article was originally published at Tryolabs’ website. It is reprinted here with the permission of Tryolabs. In the ever-evolving landscape of natural language processing, the advent of Large Language Models (LLMs) has ushered in a new era of possibilities and challenges. While these models showcase remarkable capabilities in generating human-like text, the potential for
New AI Model Offers Cellular-level View of Cancerous Tumors
This blog post was originally published at NVIDIA’s website. It is reprinted here with the permission of NVIDIA. Researchers studying cancer unveiled a new AI model that provides cellular-level mapping and visualizations of cancer cells, which scientists hope can shed light on how—and why—certain inter-cellular relationships triggers cancers to grow. BioTuring, a San Diego-based startup,

D3 Embedded Partners with Silicon Highway to Provide Rugged Camera Solutions to Europe
Rochester, NY – February 12, 2025 – D3 Embedded today announced its partnership with Silicon Highway, a leading European distribution company specializing in embedded AI edge solutions, to accelerate the delivery of high-performance rugged cameras to the European market. This partnership will allow D3 Embedded to leverage Silicon Highway’s local expertise and knowledge of the

The Intersection of AI and Human Expertise: How Custom Solutions Enhance Collaboration
This blog post was originally published at Digica’s website. It is reprinted here with the permission of Digica. Artificial Intelligence-based solutions have become increasingly prevalent, transforming industries, businesses, and daily life. However, rather than completely replacing human expertise, the most effective approach lies in creating a synergy between human knowledge, experience and intuition alongside AI’s

SAM 2 + GPT-4o: Cascading Foundation Models via Visual Prompting (Part 1)
This article was originally published at Tenyks’ website. It is reprinted here with the permission of Tenyks. In Part 1 of this article we introduce Segment Anything Model 2 (SAM 2). Then, we walk you through how you can set it up and run inference on your own video clips. Learn more about visual prompting

DeepSeek-R1 1.5B on SiMa.ai for Less Than 10 Watts
February 18, 2025 09:00 AM Eastern Standard Time–SAN JOSE, Calif.–(BUSINESS WIRE)–SiMa.ai, the software-centric, embedded edge machine learning system-on-chip (MLSoC) company, today announced the successful implementation of DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-1.5B on its ONE Platform for Edge AI, achieving breakthrough performance within an unprecedented power envelope of under 10 watts. This implementation marks a significant advancement in efficient, secure

From Brain to Binary: Can Neuro-inspired Research Make CPUs the Future of AI Inference?
This article was originally published at Tryolabs’ website. It is reprinted here with the permission of Tryolabs. In the ever-evolving landscape of AI, the demand for powerful Large Language Models (LLMs) has surged. This has led to an unrelenting thirst for GPUs and a shortage that causes headaches for many organizations. But what if there

From Seeing to Understanding: LLMs Leveraging Computer Vision
This blog post was originally published at Tryolabs’ website. It is reprinted here with the permission of Tryolabs. From Face ID unlocking our phones to counting customers in stores, Computer Vision has already transformed how businesses operate. As Generative AI (GenAI) becomes more compelling and accessible, this tried-and-tested technology is entering a new era of
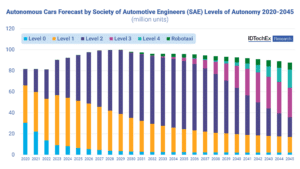
Autonomous Cars are Leveling Up: Exploring Vehicle Autonomy
When the Society of Automotive Engineers released their definitions of varying levels of automation from level 0 to level 5, it became easier to define and distinguish between the many capabilities and advancements of autonomous vehicles. Level 0 describes an older model of vehicle with no automated features, while level 5 describes a future ideal

Introducing Qualcomm Custom-built AI Models, Now Available on Qualcomm AI Hub
This blog post was originally published at Qualcomm’s website. It is reprinted here with the permission of Qualcomm. We’re thrilled to announce that five custom-built computer vision (CV) models are now available on Qualcomm AI Hub! Qualcomm Technologies’ custom-built models were developed by the Qualcomm R&D team, optimized for our platforms and designed with end-user applications
The Ultimate Guide to Depth Perception and 3D Imaging Technologies
This blog post was originally published at e-con Systems’ website. It is reprinted here with the permission of e-con Systems. Depth perception helps mimic natural spatial awareness by determining how far or close objects are, which makes it invaluable for 3D imaging systems. Get expert insights on how depth perception works, the cues involved, as

